Introduction
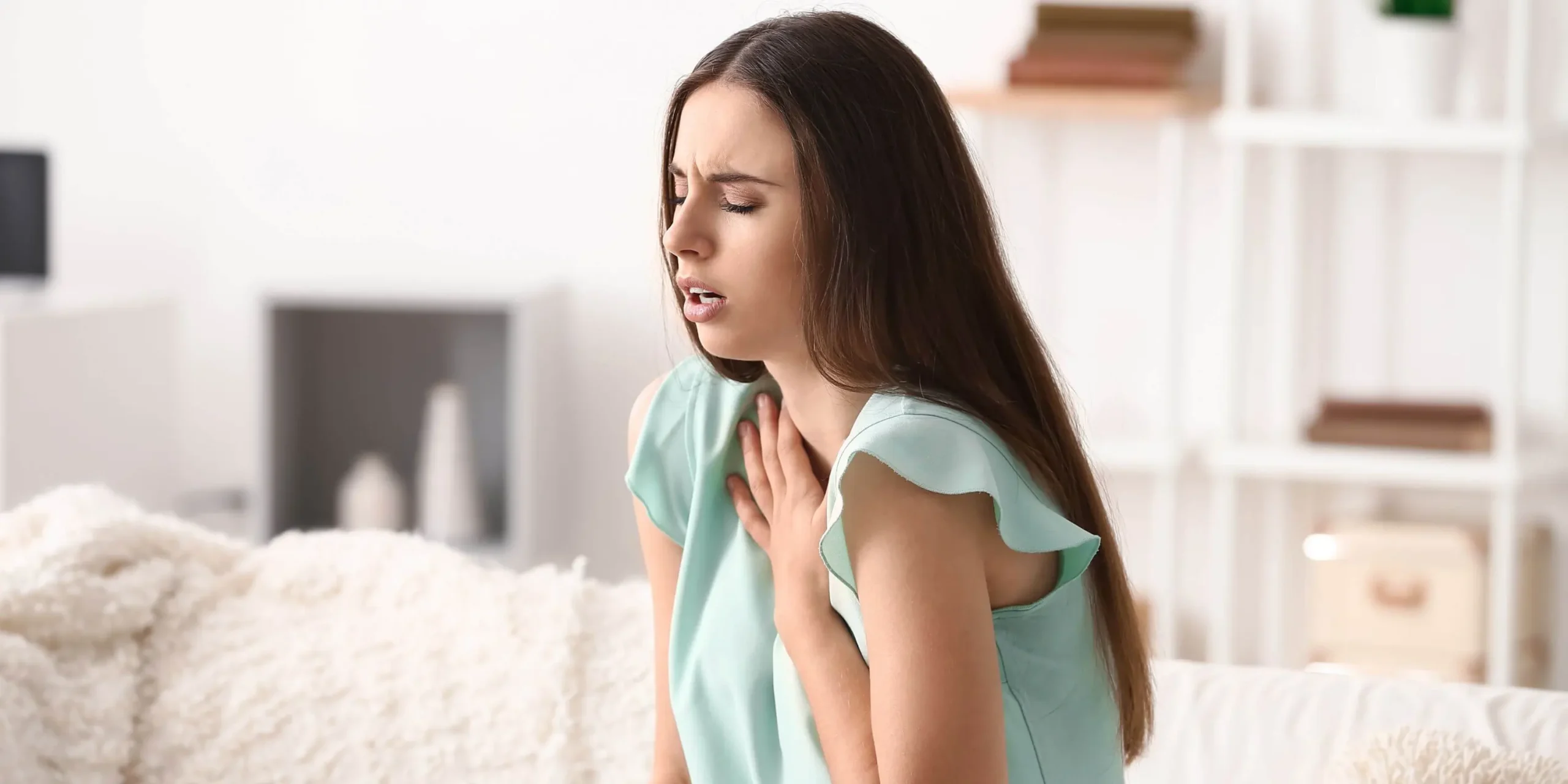
Asthma, a chronic respiratory condition, affects millions of people worldwide. While medical interventions and lifestyle changes play crucial roles in managing this, the impact of diet often goes unnoticed. In this article, we delve into the intricate relationship between diet and asthma management, exploring how dietary choices can influence this symptoms and overall lung health.
The Link Between Diet and Asthma
Understanding Asthma Triggers
Asthma triggers vary from person to person but commonly include allergens, air pollutants, and respiratory infections. However, emerging research suggests that diet may also trigger or alleviate this symptoms.
Identifying Potential Dietary Triggers
Certain foods, such as dairy, processed meats, and sulfite-containing foods, have been linked to this exacerbations in some individuals. Understanding these triggers is essential for effective asthma management.
The Role of Inflammatory Foods
Understanding Inflammation in Asthma
Inflammation plays a central role in this pathogenesis, contributing to airway constriction and respiratory symptoms. Consumption of inflammatory foods can exacerbate this inflammation, worsening asthma symptoms.
Asthma Treatments: Red asthma Inhaler, Blue Inhaler for asthma
Avoiding Inflammatory Foods
Processed foods high in trans fats, refined sugars, and artificial additives promote inflammation in the body. Minimizing their intake can help reduce inflammation and alleviate this symptom.
Importance of Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Counteracting Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between antioxidants and free radicals, contributes to airway inflammation and severity. Antioxidant-rich foods help neutralize free radicals, mitigating oxidative stress and supporting lung health.
Incorporating Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds are rich sources of antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and flavonoids. Including these foods in your diet can help reduce related inflammation and improve respiratory function.
The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Omega-3s
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, possess potent anti-inflammatory properties. Incorporating omega-3-rich foods into your diet can help reduce airway inflammation and enhance lung function in individuals with asthma.
Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Cold-water fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3s. Plant-based sources such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts also provide ample amounts of these beneficial fats.
The Gut-Lung Axis: Importance of Gut Health
Exploring the Gut Microbiota
Imbalances in gut bacteria may exacerbate these symptoms and inflammation.
Promoting Gut Health Through Diet
Consuming fiber-rich foods, fermented foods, and prebiotics supports a healthy gut microbiome. These dietary strategies can help modulate immune function and reduce related inflammation.
Asthma and Exercise
Regular exercise is important for overall health and well-being, but it can pose challenges for people with asthma. With proper precautions and management strategies, however, most people with asthma can safely participate in physical activity and enjoy its many benefits.
Benefits of exercise
Exercise offers numerous health benefits for people with this , including improved lung function, increased cardiovascular fitness, reduced stress, and better overall quality of life. It can also help control weight and reduce the risk of other chronic diseases.
Precautions for asthmatics
Before starting an exercise program, it’s important for people with this to talk to their healthcare provider about their this control and any concerns they may have. Your healthcare provider can help you develop an exercise plan that’s safe and appropriate for your individual needs and abilities.
Asthma and Pregnancy
Managing asthma during pregnancy requires special considerations to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby. With proper management and medical care, most women with asthma can have a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Medication Management for Asthma
Medications play a key role in controlling asthma symptoms and preventing exacerbations. Inhalers and nebulizers are commonly used to deliver medication directly to the lungs. There are two main types of asthma medications: controller medications, which are taken daily to prevent symptoms, and rescue medications, which are used as needed to relieve sudden symptoms.
Inhalers and Nebulizers
Inhalers and nebulizers are portable devices that deliver medication in the form of a mist or spray, allowing it to reach the lungs quickly and effectively. They are available in different types, including metered-dose inhalers, dry powder inhalers, and soft mist inhalers.
Controller vs. Rescue Medications
Controller medications, such as corticosteroids and long-acting beta-agonists, work to reduce inflammation and prevent this symptoms from occurring. Rescue medications, such as short-acting beta-agonists, provide quick relief during asthma attacks.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Asthma
In addition to medication, making certain lifestyle changes can help individuals better manage their asthma and reduce the frequency of symptoms.
Diet and Nutrition
Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall respiratory health. Avoiding foods that may trigger asthma symptoms, such as dairy, processed foods, and sulfite-containing foods, is also advisable.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise is important for maintaining lung function and cardiovascular health. However, individuals with asthma should choose activities that are less likely to trigger symptoms, such as swimming, walking, or cycling, and always use a rescue inhaler before exercising if necessary.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diet plays a significant role in this management, influencing inflammation, oxidative stress, and immune function. By making mindful dietary choices, such as avoiding inflammatory foods, incorporating antioxidant-rich foods, and consuming omega-3 fatty acids, individuals with this can better control their symptoms and improve lung health.